Microdistrict in the structure of the city
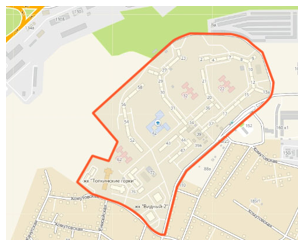
Pic. 1 Topkinsky microdistrict. 2018
District residential units The Topkinsky microdistrict is part of the Znamensky suburb of Irkutsk. Refers to the right-bank administrative district of the city. Area 15.4 ha. The project was developed at the Irkutskgrazhdanproekt Institute by architects L. F. Antipin and V. V. Grigoriev in 1982. The residential district “Marat” is located on the northern outskirts of Irkutsk (Pic. 1). Its territory is limited on the western side of a large industrial. a zone that cuts the district from the Angara, on the east – a cemetery, and on the north and south sides it is characterized by a sharp drop in relief (Znamenskaya Gora and Topkinskaya Pad). Topkinskoye is located near the large forested slopes of the Topkinskaya Pad. The building was solved by several enlarged groups of residential buildings of different floors (3-, 4-, 5-, 9-storey), both panel and brick, block – in sections, across the relief, which creates a certain plastic space. In the basement floors, in places of elevation relief, various service facilities have been designed. A school, childcare facilities and other facilities have been built in the microdistrict. The southwestern part of the district continues to be built up with Topkinsky Gorki residential complexes (commissioning of the second construction phase is expected in 2018) and Vidniy is put into operation on November 3, 2017. [1].
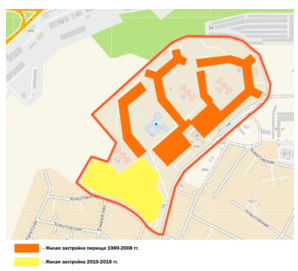
Pic. 2 Scheme of development of microdistrict Topkinsky
The construction of the microdistrict began in 1989. It presents the typical series 1-464 and 1-135 in 5 floors, and 1-306 in 9 floors, designed specifically for areas with seismic activity of 7-8 points (Pic. 2). Buildings of this type built up the central and north-eastern part of the microdistrict [2]. From the beginning of the 2000s to the present day, the southwestern part of the microdistrict has been built up with multi-storey buildings from 9 to 17 floors [3].


Basic building morphotype
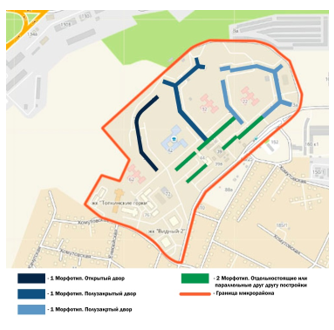
Pic. 8 Designations of building morphotypes
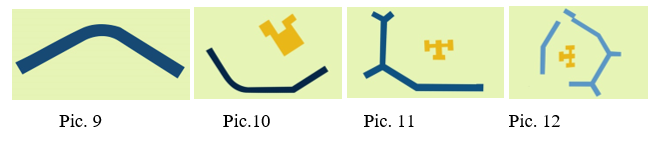
In this microdistrict, 2 basic morphotypes of development can be distinguished. One of them is an L-shaped module (Pic. 9), open (Pic. 10), and half-closed types (Pic. 11,12). The microdistrict is located on a high hill, therefore, a building morphotype is used that forms a cascade down the slope and forms a kind of retaining wall for each next “step”. It is precisely because of the location on a complex terrain that the module strives for “rounding”; it bends around the steps of a hill, forming expanding rings in plan. The district is even now quite distant from the center and from the social infrastructure facilities, which is why in each courtyard formed by the L-shaped module there are social municipal facilities – a comprehensive school, an art school, and a kindergarten (Pic. 10-12, marked in yellow). Thus, the module in each of the 3 options has inside not only a courtyard, but also a public institution. Another module is building on 1 side (Pic. 13), or building in parallel on 2 sides (Pic. 14). The houses located inside this module are located in the western part of the microdistrict and form a certain entrance group, “open” the microdistrict for all entering. It is within this module that a small sales area is formed.
Conclusion
Based on the analysis of the data, the following conclusions can be drawn:
- Morphotypes of this building can be considered obsolete since it is impossible to make positive changes in them without disturbing the comfort of the environment.
- The principles by which morphotypes evolved during perestroika and earlier should be taken into account when designing further development in order to comply with the principle of architectural hierarchy and general harmony.
List of sources used
- 1. Topkinsky microdistrict (Irkutsk) [Electronic resource] http://irkipedia.ru/content/topkinskiy_mikrorayon_irkutsk (21.11.18)
- N.P. Rozanov, Large-panel housing construction, Moscow, Stroyizdat, 1982, 224 pages, pic.
- I.A. Azizyan, L.I. Kirillova, Architectural Ensemble as a Form of Synthesis Implementation. Sat scientific tr. – M.: VNIITAG, 1990. – 127 pages

